The customer journey refers to the complete experience a customer has with a brand, from the moment they first become aware of it to the point where they become a loyal advocate. Rather than focusing on isolated touchpoints, it looks at how customers think, feel, and act across every interaction. Businesses use customer journeys to understand behaviour, identify friction points, and design more meaningful experiences.
For example, a customer journey could track how someone discovers a brand through social media, compares options on a website, makes a purchase, and later returns for repeat business or referrals. Mapping this journey helps organisations align marketing, sales, and service efforts around real customer needs.
In this article, we will explain what the customer journey is, explore its key stages, highlight its benefits, and walk through how to map it effectively. We will also compare the customer journey with the marketing funnel and explain how both can work together.
What Is the Customer Journey?
The customer journey is a visual or strategic representation of every interaction a customer has with a brand across channels and over time. It is commonly used by marketing, customer experience, product, and service teams to improve engagement, conversion, and retention.
Key Components of the Customer Journey
- Customer personas: Profiles that represent different customer types, based on behaviours, needs, and motivations
- Touchpoints: All interactions customers have with a brand, such as ads, websites, emails, or customer support. Effective communication skills are essential at each touchpoint to ensure messaging is clear, consistent, and aligned with customer expectations
- Channels: The platforms where interactions occur, including digital, physical, and human-led channels
- Customer actions: The steps customers take at each stage, such as researching, comparing, purchasing, or providing feedback
- Emotions and expectations: How customers feel at each stage and what they expect from the brand
- Pain points and opportunities: Areas where customers face friction, alongside opportunities to improve the experience
5 Key Stages Of Customer Journey
The customer journey typically follows a series of stages that reflect how relationships with brands develop over time. Understanding these stages helps organisations tailor messages, content, and experiences more effectively.
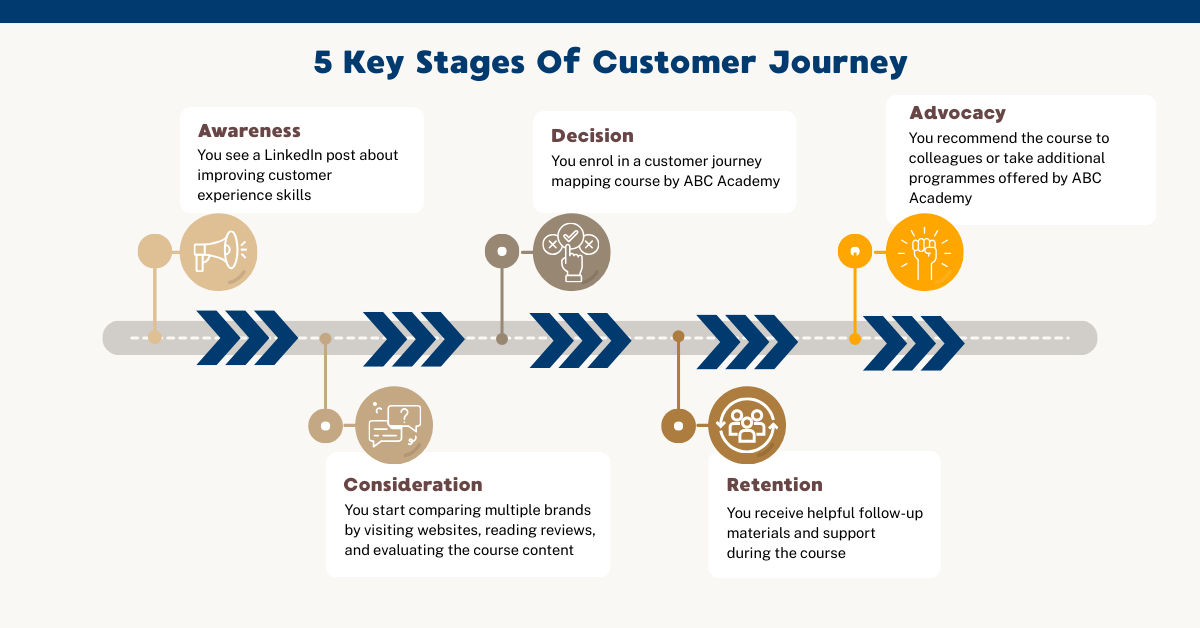
Awareness
At this stage, customers realise they have a need or problem and become aware of a brand for the first time. This may happen through social media, search engines, advertisements, or word of mouth.
Example: A professional sees a LinkedIn post about improving customer experience skills.
Learn how to drive customer awareness through social media with Digital Marketing – Social Media Marketing.
Consideration
Customers actively research and compare options to decide which solution best meets their needs. They may read reviews, download resources, or attend webinars.
Example: In an online business context, customers may compare multiple brands within minutes by visiting websites, reading reviews, and evaluating digital content side by side.
Strengthen how your brand connects and stands out with Foundations Of Brand Storytelling.
Decision
The customer is ready to make a purchase or commitment. Clear value propositions, pricing transparency, and trust signals play a key role here.
Example: The customer enrols in a customer journey mapping course.
Learn strategies that move customers from intent to action with Luxury Sales: Learn Advanced Sales Strategies Tailored for the Luxury Market.
Retention
After the purchase, the focus shifts to delivering value and building long-term relationships. Ongoing support, communication, and engagement are critical.
Example: The customer receives helpful follow-up materials and support during the course.
Build long-term customer loyalty with Customer Loyalty & Relationship Management (CRM): Strategies for Building Long-Term Value.
Advocacy
Satisfied customers return, renew, or recommend the brand to others. Advocacy is built through consistently positive experiences that encourage customers to share their experiences organically.
Example: The customer recommends the course to colleagues or takes additional programmes.
Learn what motivates customers to return and recommend with Customer Loyalty: Gaining Insights from Consumer Psychology and Behavioural Science.
Benefits Of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping helps organisations move beyond assumptions and base decisions on real customer experiences. It provides clarity on how customers interact with a brand and where improvements can make the biggest impact.
- Improves customer experience
By identifying friction points, businesses can remove obstacles and create smoother, more intuitive experiences.
- Aligns teams around the customer
Journey maps provide a shared view that helps marketing, sales, and service teams work towards common goals.
- Increases conversion rates
Understanding customer decision-making enables more relevant messaging and timely interventions.
- Enhances customer retention
Addressing post-purchase needs improves satisfaction, builds trust and long-term relationships, and encourages repeat engagement.
- Identifies gaps across channels
Journey mapping highlights inconsistencies between digital and offline experiences.
- Supports data-driven decision-making
When combined with customer data, journey maps help prioritise initiatives with the greatest impact.
How To Map Out The Customer Journey Process
Mapping the customer journey involves combining research, data, and cross-functional input to understand how customers experience a brand across all touchpoints, both online and offline. Professionals looking to build these skills can explore SMU Academy’s Data-Driven Customer Journey Mapping course, which focuses on using data and insights to design effective journeys.
Below is a practical, step-by-step guide that marketing professionals can apply in real-world scenarios.

Step 1: Define Your Objective
Start by clearly defining what you want the journey map to achieve. This could include improving lead conversion, reducing drop-offs at a specific stage, enhancing onboarding, or increasing retention. A clear objective ensures the journey remains focused and relevant.
Step 2: Identify Customer Personas
Identify the primary customer persona you are mapping for. Focus on one persona at a time, based on role, needs, motivations, and behaviours. This prevents overgeneralisation and allows for more precise insights.
Step 3: Map Customer Touchpoints
Document every touchpoint where customers interact with your brand, including paid ads, social media, websites, emails, sales calls, customer service, onboarding materials, and post-purchase communications. The customer journey spans across departments and channels, not just marketing-owned touchpoints.
Step 4: Capture Customer Actions
Detail what customers do at each stage and touchpoint. This includes actions such as searching for information, comparing alternatives, signing up, making enquiries, or seeking support. Understanding these actions helps identify moments of influence and decision-making.
Step 5: Analyse Emotions
Go beyond actions to understand how customers feel at each stage. Identify moments of confidence, confusion, frustration, or satisfaction. Emotional insights often reveal why customers progress, pause, or drop off.
Step 6: Integrate Data
Validate assumptions using quantitative and qualitative data such as web analytics, CRM data, surveys, interviews, and feedback. Data helps prioritise issues and ensures the journey reflects real behaviour rather than internal perceptions.
Tools powered by AI in marketing can further enhance this process by uncovering insights that may not be immediately visible through manual analysis, such as predicting drop-off points or identifying high-intent moments.
Step 7: Identify Opportunities for Improvement
Highlight gaps, pain points, and missed opportunities across touchpoints. These insights can inform content optimisation, channel improvements, messaging refinement, or process changes that enhance the overall experience.
Best Practices When Mapping Out The Customer Journey Process
Effective customer journey mapping requires both strategic thinking and attention to detail. Following best practices helps ensure the journey remains useful and relevant.
- Focus on the customer perspective: Avoid designing journeys based solely on internal processes or organisational structure
- Keep journeys clear and focused: A simple, well-defined journey is more actionable than an overly complex one
- Use real data, not assumptions: Validate insights with behavioural data, feedback, and research wherever possible
- Collaborate across teams: Involve stakeholders from marketing, sales, service, and product to gain a complete view
- Review and update regularly: Customer behaviours and expectations evolve, so journeys should be revisited over time
- Link insights to action: Ensure journey findings translate into clear priorities and measurable improvements
Customer Journey vs Marketing Funnel
While both concepts focus on guiding customers towards conversion, they serve different purposes and offer distinct perspectives. Understanding how they differ and complement each other helps marketing professionals design more effective strategies.
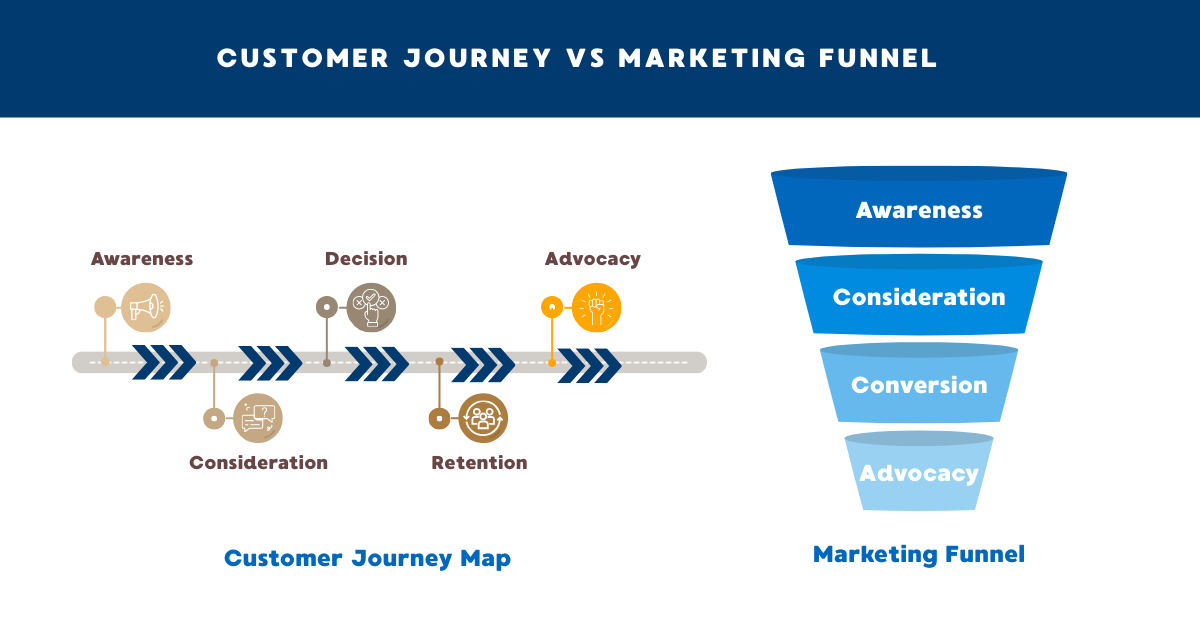
Key Differences
How They Work Together
Used together, the marketing funnel and customer journey provide both performance and experience insights. The funnel helps marketers track where customers drop off and assess conversion effectiveness, while the customer journey explains why those drop-offs occur.
For example, a funnel may show low conversion during the consideration stage. Journey mapping may reveal that customers encounter inconsistent messaging across channels or lack clarity at key touchpoints. By aligning funnel metrics with journey insights, marketing professionals can optimise both conversion outcomes and customer experience holistically.
Building Stronger Experiences Through The Customer Journey
Understanding the customer journey enables organisations to design experiences that are relevant, consistent, and customer-centric. By mapping every stage from awareness to loyalty, businesses gain insight into what customers need, where they struggle, and how value can be delivered more effectively.
Customer journey mapping supports better alignment across teams, stronger engagement, and more sustainable growth. When combined with data and continuous improvement, it becomes a powerful tool for improving both customer satisfaction and business performance.
For professionals looking to deepen their capabilities, structured learning can provide the frameworks and practical skills needed to apply customer journey mapping effectively in real-world contexts.
Browse SMU Academy’s programmes to build practical customer journey mapping skills that support conversion, retention, and long-term customer value.